Best Free Schema Registry Solutions for Modern Data Streams
 Community Contribution
Community ContributionTable of contents
- Key Takeaways
- Schema Registry Basics
- Top Open-Source Schema Registry Projects
- Schema Registry Comparison
- Choosing an Open-Source Schema Registry
- Implementation Tips
- FAQ
- What is a schema registry used for?
- Which schema formats do most registries support?
- How does schema evolution work in a registry?
- Can small teams deploy a schema registry easily?
- Is a schema registry necessary for Kafka?
- How do registries handle security?
- What happens if a schema change breaks compatibility?
- Can a schema registry run in the cloud?

Many organizations rely on open-source schema registry solutions such as Confluent Schema Registry, Karapace, AWS Glue Schema Registry, Redpanda Schema Registry, Apicurio Registry, Schema Manager, and WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry for managing schemas in data streaming environments. Confluent's Schema Registry serves as a key tool for enforcing schema validation and compatibility, while Redpanda Schema Registry offers simplicity and performance for resource-constrained teams.
Schema registries provide a centralized way to manage schema versions, enforce data contracts, ensure compatibility, and maintain data quality and governance across distributed systems.
Key Takeaways
Schema registries centralize schema management to ensure data consistency and quality in real-time streaming.
They enforce compatibility rules that prevent data corruption and service disruptions during schema changes.
Popular open-source schema registries include Confluent, Karapace, AWS Glue, Redpanda, Apicurio, Schema Manager, and WarpStream BYOC.
Choosing a schema registry depends on team size, deployment needs, and integration with streaming platforms like Kafka or cloud services.
Lightweight registries suit small teams needing simple setup, while enterprises require advanced governance and security features.
Cloud-native and hybrid environments benefit from registries that support scalability, automation, and secure multi-environment management.
Proper schema evolution strategies and monitoring help maintain smooth data pipeline operations and avoid compatibility issues.
Security features like authentication, encryption, and access control are essential to protect schema data in streaming systems.
Schema Registry Basics
What Is a Schema Registry
A schema registry acts as a centralized service for managing and storing schemas in real-time data environments. It provides a repository where teams can register, retrieve, and update schemas for data serialization formats such as Avro, JSON Schema, and Protobuf. The registry tracks schema versions and ensures that each schema change is recorded and accessible.
Key functions and components of a schema registry include:
Centralized schema management and storage for tracking schema versions.
Schema validation to confirm that data matches the defined schema format.
Compatibility checking to maintain contracts between producers and consumers.
Schema versioning and evolution support, allowing changes without breaking existing data.
Schema ID validation, which optimizes real-time payloads by referencing schema IDs instead of full schemas.
Data governance through a single repository for all schemas.
RESTful services for schema validation, storage, and retrieval.
Serializers and deserializers (serdes) that integrate with real-time streaming clients.
Integration points with platforms like Kafka, Connect, and UI tools.
These features allow producers and consumers to communicate using well-defined data contracts, which simplifies the development and maintenance of real-time data pipelines.
Why Schema Registries Matter
A schema registry plays a critical role in real-time data streaming platforms. It ensures that all data exchanged between producers and consumers follows a consistent structure. This consistency prevents data corruption and operational failures.
Without a schema registry, even a small incompatible change—such as adding a new field—can break ETL jobs, corrupt analytical datasets, or cause data loss in compliance reports.
Schema registries enforce compatibility rules, such as backward, forward, and full compatibility. They manage schema versions and validate changes before deployment. This process safeguards data integrity and business continuity. Producers register schemas before sending data, while consumers fetch schemas to deserialize messages correctly. The registry acts as a contract, providing governance and change control for all schema updates.
The registry also supports schema evolution. Teams can add new fields with default values, remove optional fields, or rename fields while maintaining compatibility. This careful management allows real-time data systems to adapt and grow without service interruptions.
Benefits for Data Streaming
Schema registries deliver measurable benefits for real-time data streaming environments:
Zero-downtime migrations and rollback capabilities reduce downtime during schema changes.
Automated schema validation and testing improve data quality by catching issues early.
Real-time monitoring and schema-aware audit logging enhance observability and compliance.
Support for multiple schema versions in parallel reduces service interruptions.
Performance improvements include latency reduction (15–25%), bandwidth savings (40–50%), and resource efficiency gains (10–20%).
Netflix, for example, uses a schema registry to process millions of real-time events per second. This approach ensures data integrity and consistent streaming experiences. By enforcing schema validation and compatibility, the registry helps organizations maintain reliable, high-quality real-time data pipelines.
Top Open-Source Schema Registry Projects
Confluent Schema Registry
Features
Confluent Schema Registry stands out as a mature and feature-rich open-source tool for managing schemas in kafka-based environments. It supports Avro, Protobuf, and JSON Schema formats, allowing teams to enforce data contracts across real-time data pipelines. The registry assigns unique IDs and version numbers to each schema version, making schema evolution and compatibility management straightforward. Users interact with the registry through REST APIs, CLI tools, and integrations with Kubernetes. Advanced compatibility modes, such as backward, forward, and full compatibility, help teams control how schemas change over time.
| Compatibility Type | Allowed Schema Changes | Compatibility Check Scope | Upgrade Priority |
| BACKWARD | Deleting fields, adding optional fields | Last schema version | Consumers |
| BACKWARD_TRANSITIVE | Deleting fields, adding optional fields | All previous versions | Consumers |
| FORWARD | Adding fields, deleting optional fields | Last schema version | Producers |
| FORWARD_TRANSITIVE | Adding fields, deleting optional fields | All previous versions | Producers |
| FULL | Adding and deleting optional fields | Last schema version | Any order |
| FULL_TRANSITIVE | Adding and deleting optional fields | All previous versions | Any order |
| NONE | All schema changes accepted | Compatibility checking off | Depends |
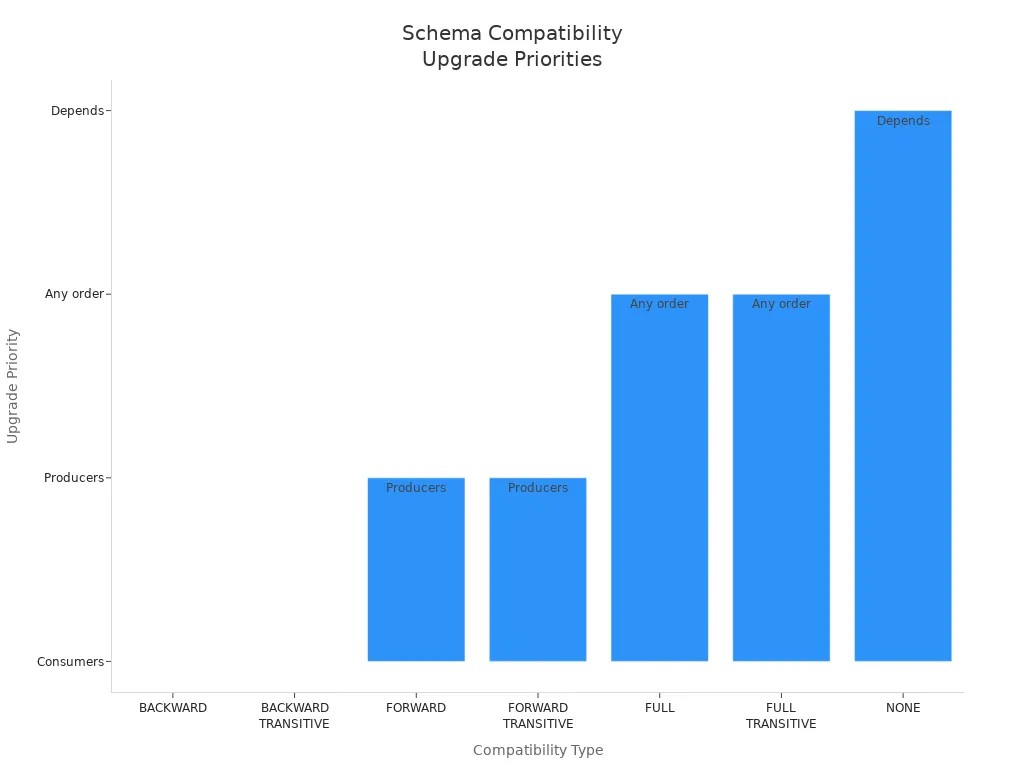
The registry also offers enterprise-grade features, including schema linking, multi-tenancy, security, logging, and metrics. These capabilities make it suitable for organizations that require robust governance and operational control.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
Rich feature set for schema management and compatibility enforcement.
Deep integration with the Confluent ecosystem and kafka.
Mature and stable open-source schema registry.
Supports multiple schema formats for real-time applications.
Cons:
Operational complexity can increase with advanced features.
Some enterprise features require a paid subscription.
May be more than needed for small teams or simple use cases.
Use Cases
Confluent Schema Registry fits enterprises that need advanced governance, multi-environment support, and seamless integration with kafka and Confluent tools. Teams managing large-scale real-time data pipelines benefit from its compatibility checks and schema evolution features. Organizations seeking strong data governance and audit capabilities often choose this registry for mission-critical streaming environments.
Karapace
Features
Karapace provides an open-source alternative for kafka users who want a lightweight schema registry. Managed by Instaclustr, Karapace supports Avro schemas and integrates directly with kafka. The registry focuses on simplicity and reliability, offering RESTful APIs for schema registration, retrieval, and validation. Karapace enables teams to manage schema versions and enforce compatibility rules without the complexity of larger platforms.
Karapace supports core schema registry functions, such as schema validation and versioning, making it a practical choice for real-time data streaming projects that use kafka.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
Fully open-source schema registry.
Simple deployment and management for kafka environments.
Reliable schema validation and compatibility enforcement.
Cons:
Smaller ecosystem compared to Confluent Schema Registry.
Fewer advanced features and integrations.
Limited support for schema formats beyond Avro.
Use Cases
Karapace suits users who need an open-source schema registry for kafka without the overhead of enterprise features. Small teams and organizations with straightforward real-time data pipelines often select Karapace for its simplicity and ease of use. It works well for projects that prioritize open-source tools and direct integration with kafka.
AWS Glue Schema Registry
Features
AWS Glue Schema Registry offers a managed, serverless solution for schema management in cloud-based data streaming architectures. The registry supports Avro, JSON Schema, and Protocol Buffers formats. It integrates with streaming platforms such as kafka, Amazon MSK, Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, Amazon Managed Service for Apache Flink, and AWS Lambda. The registry enables dynamic schema registration, allowing producers to derive schemas from event data at runtime.
| Capability Category | Description |
| Supported Schema Formats | AVRO (v1.10.2), JSON Schema (Draft-04, 06, 07), Protocol Buffers (proto2 and proto3) |
| Streaming Platform Integration | Apache Kafka, Amazon MSK, Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, Amazon Managed Service for Apache Flink, AWS Lambda |
| Schema Evolution & Compatibility | Compatibility checks and schema evolution support to handle changes in data schemas |
| Auto-registration | Schemas can be automatically registered during runtime without predefined JSON schemas |
| Serverless Operation | No infrastructure setup required; fully managed and free to use |
| Access Control | Integration with AWS IAM for fine-grained access management |
| Compression | Optional ZLIB compression to reduce storage and transfer costs |
| Data Governance | Enforces consistent data formats to improve data quality and reliability |
| Dynamic Schema Derivation | Schemas can be derived dynamically at runtime from event data |
| Cross-account Access | Supports cross-account IAM roles for centralized schema management and permission control |
The registry enforces consistent data formats and supports schema evolution and compatibility checks. AWS Glue Schema Registry also provides fine-grained access control through AWS IAM, optional ZLIB compression, and cross-account access for centralized schema management.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
Managed, serverless schema registry with no infrastructure setup.
Deep integration with AWS services and kafka.
Supports dynamic schema registration and evolution.
Fine-grained access control and cross-account management.
Cons:
Not fully open-source; tied to the AWS ecosystem.
Limited flexibility for teams outside AWS.
Advanced features may require AWS expertise.
Use Cases
AWS Glue Schema Registry serves AWS-centric teams building real-time data streaming pipelines with kafka, Kinesis, or Flink. Organizations seeking a managed schema registry with dynamic schema registration and strong access control often choose this solution. It fits cloud-native architectures that prioritize scalability, reliability, and integration with AWS services.
Redpanda Schema Registry
Features
Redpanda Schema Registry provides a unified, high-performance solution for managing schemas in modern streaming environments. The platform integrates the schema registry directly into its single-binary architecture, which also includes brokers, an HTTP proxy, and Raft consensus. This design eliminates external dependencies and reduces latency for kafka-compatible workloads. Redpanda supports Avro, Protobuf, and JSON Schema formats, enabling teams to enforce data contracts and maintain compatibility across real-time pipelines.
Key features include:
Seamless integration with Redpanda’s kafka API, allowing drop-in replacement for existing kafka schema registry deployments.
RESTful API for schema registration, retrieval, and validation.
Support for schema versioning and compatibility checks.
Built-in security features, including authentication and access control.
Automatic hardware tuning for optimal performance.
Redpanda’s implementation in C++ uses a thread-per-core model and manages memory and disk I/O directly. This approach bypasses the Linux page cache, ensuring predictable low latency and high throughput. Optimistic Raft and parallel commits enable transactions up to six times faster than traditional kafka implementations. The platform also delivers up to ten times lower tail latencies, even under heavy loads. The schema registry, as part of this unified system, supports data consistency and integration without adding overhead from external components.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
High-throughput and low-latency performance for demanding streaming workloads.
Unified platform with integrated schema registry, brokers, and consensus.
No external dependencies, simplifying deployment and operations.
Automatic hardware tuning and topic-level optimization.
Full compatibility with kafka APIs and open-source tools.
Cons:
Smaller community compared to legacy kafka projects.
Some advanced features may require familiarity with Redpanda’s architecture.
Limited to Redpanda and kafka-compatible environments.
Use Cases
Redpanda Schema Registry fits organizations that need a high-performance, open-source schema registry for real-time data streaming. Teams running latency-sensitive applications, such as financial trading or telemetry analytics, benefit from its predictable performance. Companies seeking to simplify their infrastructure by reducing external dependencies often choose Redpanda. The registry also supports hybrid deployments where teams want to migrate from kafka to a more efficient platform without changing their existing schema management workflows.
Apicurio Registry
Features
Apicurio Registry is an open-source schema registry designed for flexibility and extensibility. It supports multiple data formats, including Avro, JSON Schema, and Protobuf, making it suitable for diverse streaming and event-driven architectures. Apicurio Registry provides a REST API, a web-based user interface, and CLI tools for managing schemas. The platform integrates with kafka, Kafka Connect, and other messaging systems, enabling seamless schema validation and compatibility enforcement.
Key features include:
Support for multiple artifact types, such as API specifications and protocol definitions, in addition to schemas.
Pluggable storage backends, including SQL databases, Kafka, and in-memory options.
Advanced compatibility rules and versioning strategies.
Role-based access control and audit logging for governance.
Integration with CI/CD pipelines for automated schema management.
Apicurio Registry’s modular design allows teams to customize storage, security, and integration options. The platform’s open-source nature encourages community contributions and rapid feature development.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
Flexible and extensible open-source schema registry.
Broad support for data formats and artifact types.
Pluggable storage and deployment options.
Active community and frequent updates.
User-friendly web interface and automation tools.
Cons:
May require additional configuration for production use.
Smaller ecosystem compared to Confluent Schema Registry.
Some advanced features may need custom development.
Use Cases
Apicurio Registry serves organizations that need a versatile, open-source schema registry for kafka and other streaming platforms. Teams managing complex event-driven systems or microservices architectures benefit from its support for multiple artifact types and integration options. The registry fits well in environments where flexibility, extensibility, and automation are priorities, such as DevOps-driven teams or those adopting CI/CD practices.
Schema Manager
Features
Schema Manager provides centralized schema management for distributed systems, focusing on schema versioning, compatibility checks, and governance. The platform supports Avro, JSON Schema, and Protobuf formats, enabling teams to enforce data contracts across kafka and other streaming platforms. Schema Manager offers REST APIs for schema registration, retrieval, and validation, along with integration points for popular open-source tools.
The registry enforces compatibility modes such as backward, forward, and full compatibility. These modes ensure that schema changes do not disrupt data serialization and deserialization between producers and consumers. By managing compatibility, Schema Manager prevents data processing errors and maintains data integrity. The platform also supports schema evolution, allowing teams to update schemas without breaking existing services.
Schema Manager centralizes schema storage and validation, ensuring that all producers and consumers use compatible schema versions. This centralization enforces schema validation at ingestion, maintaining data quality and preventing mismatches that could cause failures. The registry supports automated schema migrations integrated with CI/CD pipelines, using patterns like Expand and Contract to ensure backward compatibility and zero downtime. Schema Manager also enforces schema ownership and access controls, preventing conflicts and unauthorized changes.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
Centralized schema management and validation for distributed systems.
Strong support for schema versioning and compatibility enforcement.
Integration with CI/CD pipelines for automated schema evolution.
Access controls and audit logging for governance.
Compatible with kafka and other open-source tools.
Cons:
May require additional setup for integration with legacy systems.
Smaller user base compared to more established schema registries.
Some features may depend on community support or custom development.
Use Cases
Schema Manager fits teams that need robust schema versioning and compatibility checks in distributed microservices environments. Organizations adopting CI/CD practices benefit from automated schema migrations and validation. The registry works well for companies that prioritize data quality, governance, and continuous schema evolution across kafka and other streaming platforms. Schema Manager also supports collaboration across distributed teams by maintaining up-to-date schema documentation and enforcing clear ownership.
WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry
Features
WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry introduces a modern approach to schema management for kafka and streaming platforms. This open-source solution uses a Bring Your Own Cloud (BYOC) model, allowing organizations to deploy the registry within their own cloud environments. WarpStream agents run as stateless containers, which simplifies scaling and maintenance. The schema registry stores schemas directly in the user's object storage, while metadata coordination happens through WarpStream’s managed control plane.
The architecture separates storage from compute, using a zero disk model. This means schemas never touch intermediary disks, reducing complexity and improving reliability. All agents can handle both read and write requests, which eliminates the need for leader election and avoids bottlenecks common in traditional kafka schema registry setups. WarpStream also uses a distributed file cache with consistent hashing. This design assigns responsibility for caching specific schema files to certain agents, which reduces object storage API calls and lowers latency.
Zone-aware routing ensures that clients connect to agents in the same availability zone. This feature helps organizations avoid inter-zone networking fees and improves performance. The registry also separates schema data from metadata, storing schemas in object storage and managing schema IDs and other metadata in the control plane. This separation enables high scalability and resilience.
| Feature / Aspect | Description |
| Deployment Model | BYOC approach with stateless agents as containers in the user's cloud; schemas stored in object storage; metadata managed by WarpStream’s control plane. |
| Stateless Agents | Easy scaling by adding containers during read spikes; no complex state management required. |
| Zero Disk Architecture | Schemas live directly in object storage; no intermediary disks; separates storage from compute. |
| Equal Agents for Read/Write | All agents can handle both read and write requests; no leader election delays. |
| Distributed File Cache | Consistent hashing assigns caching responsibility for schema files to specific agents; reduces object storage API calls and latency. |
| Zone-aware Routing | Clients connect to agents in the same availability zone; avoids inter-zone networking fees and optimizes performance. |
| Separation of Data and Metadata | Schemas stored in object storage; metadata managed by WarpStream’s control plane; enables scalability and resilience. |
WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry supports Avro, JSON Schema, and Protobuf formats. It integrates seamlessly with kafka and other open-source tools, making it a flexible choice for teams that want to manage schemas efficiently in distributed environments.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
Open-source schema registry with a BYOC deployment model.
Stateless agents allow for easy scaling and high availability.
Zero disk architecture reduces operational complexity.
All agents can process both read and write requests, eliminating leader bottlenecks.
Distributed file cache and zone-aware routing improve performance and reduce costs.
Strong integration with kafka and compatibility with other open-source tools.
Cons:
Requires object storage and cloud infrastructure, which may not suit all organizations.
Newer project with a smaller community compared to established kafka schema registry solutions.
Some advanced features depend on WarpStream’s managed control plane.
Note: Teams should evaluate their cloud readiness and object storage capabilities before adopting WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry.
Use Cases
WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry fits organizations that need a scalable, cloud-native schema registry for kafka and streaming workloads. Teams running high-throughput pipelines benefit from the stateless agent model, which allows rapid scaling during traffic spikes. Companies with multi-zone or multi-region deployments can leverage zone-aware routing to optimize costs and performance.
This registry works well for businesses that want to keep control of their data within their own cloud while using open-source tools. It also suits teams looking to modernize their kafka infrastructure without adding operational overhead. WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry provides a robust solution for managing schemas in real-time data environments, supporting both rapid growth and strict governance requirements.
Schema Registry Comparison
Supported Formats
A schema registry must support multiple serialization formats to meet the needs of modern data streaming. Each registry offers different levels of compatibility with popular formats. The table below shows the main formats supported by leading schema registry solutions:
| Schema Registry | Avro | Protobuf | JSON Schema | Other Formats |
| Confluent | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | - |
| Karapace | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | - |
| AWS Glue | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | - |
| Redpanda | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | - |
| Apicurio | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | API Specs, etc. |
| Schema Manager | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | - |
| WarpStream BYOC | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | - |
Confluent Schema Registry stands out with dedicated serializers and deserializers for Avro, Protobuf, and JSON Schema. These tools help teams enforce schema validation in real-time data pipelines. Apicurio Registry adds flexibility by supporting additional artifact types, such as API specifications. Most registries focus on Avro, Protobuf, and JSON Schema, which are the most common formats in real-time data streaming. Teams should select a schema registry that matches their preferred serialization format to ensure smooth integration with kafka and other platforms.
Integration
Integration capabilities play a key role in choosing a schema registry for real-time data streaming. Leading registries offer REST APIs, CLI tools, and SDKs for popular programming languages. These features allow developers to register, retrieve, and validate schemas easily.
Confluent Schema Registry and Redpanda Schema Registry provide seamless integration with kafka, making them ideal for teams building real-time data pipelines.
AWS Glue Schema Registry connects with Amazon MSK, Kinesis, Flink, and Lambda, supporting cloud-native architectures.
Apicurio Registry and Schema Manager offer integration with kafka, Kafka Connect, and CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated schema management.
WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry uses stateless agents and object storage, allowing flexible deployment in cloud environments.
Tip: Teams should check if the schema registry supports their chosen data streaming platform and programming language. This step ensures that schema validation and evolution work smoothly in real-time applications.
Security
Security remains a top priority for any schema registry in a real-time environment. Leading solutions implement strong authentication, encryption, and authorization features to protect schema data.
Encryption uses TLS to secure data in transit between clients and the registry.
Authorization relies on Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), LDAP group-based permissions, and Access Control Lists (ACLs).
Some registries support client-side field-level encryption for sensitive schema fields.
Advanced options include custom Key Management Service (KMS) drivers and security plugins.
These security mechanisms help organizations maintain data integrity and privacy in real-time data pipelines. Teams should configure authentication and encryption settings to match their compliance requirements. A secure schema registry ensures that only authorized users can register, update, or retrieve schemas, reducing the risk of data breaches in kafka and other streaming systems.
Scalability
Scalability stands as a core requirement for any schema registry in modern data streaming. As organizations grow, they often add more producers and consumers to their real-time pipelines. This growth increases the number of schema changes and the complexity of managing data contracts. A schema registry addresses these challenges by acting as a centralized hub for schema management. It enforces compatibility rules and supports versioning, which allows multiple schema versions to coexist. This capability prevents breaking changes and ensures that real-time data pipelines remain reliable as they scale.
In large-scale environments, manual schema management can lead to data corruption or pipeline failures. A registry automates schema detection and validation, reducing the risk of human error. For example, in a kafka deployment, producers register schemas with the registry, and consumers retrieve them using schema IDs. This process optimizes performance because only the schema ID travels with each message, not the entire schema. As a result, the system handles millions of events per second without bottlenecks.
Many schema registry solutions, such as those integrated with kafka or platforms like Tinybird, support live schema migrations. These migrations allow teams to evolve schemas without downtime. Automation plays a key role in this process. Automated schema verification and evolution help maintain data integrity and avoid disruptions during upgrades or changes. Production-grade architectures rely on these features to ensure smooth operation at scale.
Some registries, like Redpanda Schema Registry and WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry, use stateless agents or unified architectures. These designs simplify scaling by allowing teams to add or remove agents as needed. The registry remains available and responsive, even during traffic spikes. Zone-aware routing and distributed caching further enhance scalability by reducing latency and optimizing resource usage.
Note: While most schema registry documentation highlights operational best practices, explicit performance benchmarks are rare. The focus remains on preventing disruptions and enabling reliable, scalable real-time data pipelines.
Community Support
Community support influences the long-term success of any schema registry project. A strong community provides documentation, troubleshooting help, and regular updates. Confluent Schema Registry benefits from a large user base and active contributors. This support ensures frequent releases, bug fixes, and a wealth of tutorials. Kafka users often find answers quickly due to the registry’s popularity.
Karapace and Apicurio Registry also maintain active open-source communities. Developers contribute new features and respond to issues on platforms like GitHub. These projects offer forums, chat channels, and public roadmaps. Redpanda Schema Registry, while newer, has seen rapid growth in its user community. The team provides detailed guides and responsive support channels.
AWS Glue Schema Registry receives support through AWS forums and official documentation. While not fully open-source, it benefits from AWS’s extensive knowledge base and customer service. Schema Manager and WarpStream BYOC Schema Registry have smaller but growing communities. Users can access documentation, submit issues, and request features through their respective repositories.
| Schema Registry | Community Size | Documentation | Support Channels |
| Confluent | Large | Extensive | Forums, GitHub, Slack |
| Karapace | Medium | Good | GitHub, Forums |
| AWS Glue | Large (AWS) | Extensive | AWS Forums, Docs |
| Redpanda | Growing | Detailed | GitHub, Discord |
| Apicurio | Medium | Good | GitHub, Chat |
| Schema Manager | Small | Adequate | GitHub |
| WarpStream BYOC | Small | Adequate | GitHub, Docs |
A vibrant community accelerates learning and problem-solving. Teams should consider the level of community engagement when selecting a schema registry for real-time streaming projects.
Choosing an Open-Source Schema Registry
Small Teams
Small teams often face limited resources and need rapid development cycles. Selecting an open-source schema registry that matches these constraints can help them maintain data quality without adding operational overhead. Lightweight registries, such as Karapace or Apicurio Registry, offer simple deployment and low resource consumption. These solutions allow teams to focus on building features rather than managing infrastructure.
The following table highlights key considerations for small teams when choosing a schema registry:
| Resource Aspect | Key Considerations for Small Teams with Limited Resources and Rapid Development |
| Memory | Lightweight registry uses minimal memory; ~1GB heap supports thousands of schemas. |
| CPU | Light CPU usage; more cores improve concurrency for compatibility checks. |
| Disk | Minimal disk needs; schemas stored in Kafka, only logs use disk space. |
| Network | Fast, reliable network required; avoid multi-data-center setups for stability. |
| JVM | Use latest JDK with G1 garbage collector for performance and security. |
| Deployment | Simple Kafka-based leader election; avoid complex cluster management. |
Tip: Small teams should prioritize ease of deployment and low maintenance. Choosing an open-source registry with a simple setup can help them move quickly and avoid unnecessary complexity.
Enterprise Deployments
Enterprises require advanced governance, compliance, and scalability from their schema registry. Open-source solutions like Confluent Schema Registry and Cloudera Data Lake provide features that support strict data governance and regulatory requirements. These registries capture and store schema definitions, enforce access control, and offer encryption for data at rest and in motion. Enterprises also benefit from audit logging, metadata management, and integration with single sign-on systems.
Key features for enterprise schema registry deployments include:
Automatic capture and storage of schema and metadata definitions for governance.
Dynamic, role-based access control and attribute-based security policies.
Encryption for data at rest and in transit, with auditing and key management.
Metadata management tools for compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Single sign-on integration for secure access.
The following table compares essentials and advanced packages for enterprise-grade schema registry solutions:
| Feature | Essentials Package | Advanced Package (Enterprise-grade) |
| Schema Registry Availability | Yes | Yes |
| SLA (Schema Registry) | 99.5% | 99.99% |
| Data Rules Support | No | Yes |
| Number of Data Contracts | 100 | 20,000 |
| Number of Schema Links | 10 | 100 |
| Stream Catalog Tags | Yes | Yes |
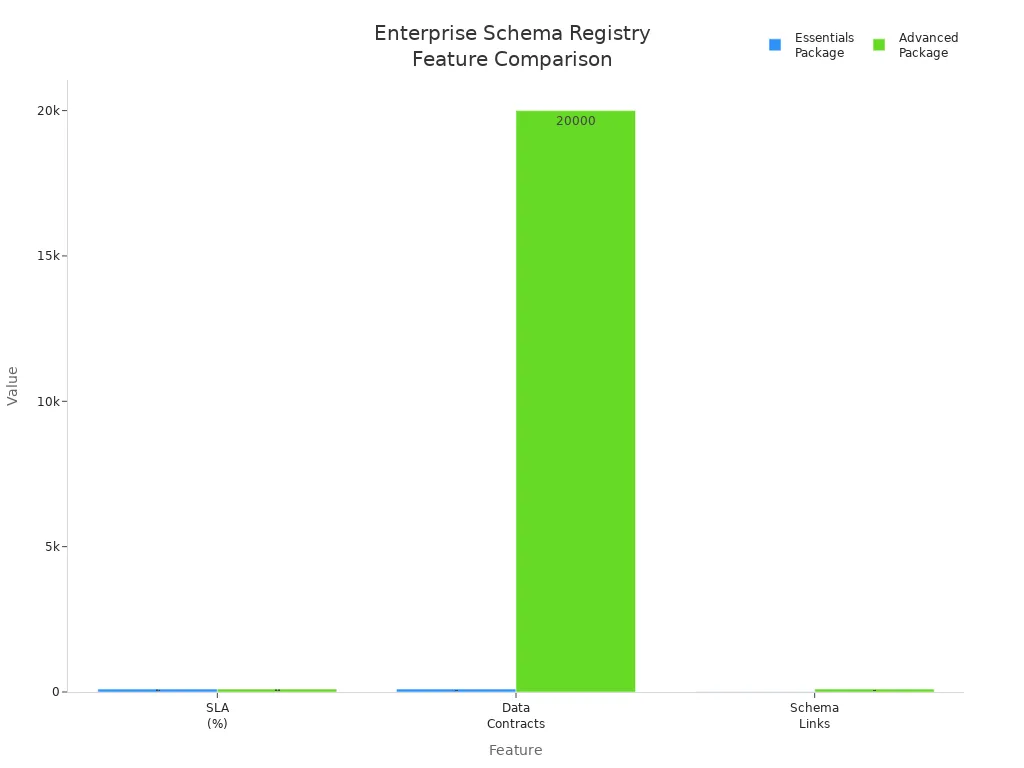
Note: Enterprises should select a schema registry that aligns with their compliance and governance needs. Advanced packages offer higher availability, more data contracts, and enhanced security features.
Cloud-Native Use
Cloud-native teams need a schema registry that integrates seamlessly with managed streaming services and supports dynamic scaling. Open-source registries like Apicurio Registry and managed options such as AWS Glue Schema Registry or Azure Schema Registry provide centralized schema management for event streaming applications. These registries ensure data compatibility and consistency across cloud environments.
A cloud-native schema registry supports schema evolution and validation, allowing teams to adapt to changing data formats. Integration with Kafka, Event Hubs, and other SDK-based applications enables efficient data exchange. Features like auto-scaling and rapid deployment simplify infrastructure management and reduce operational burden.
DoubleCloud’s managed Kafka service, for example, includes a built-in schema registry that maintains data consistency as data formats evolve. This approach supports cloud-native architectures by enabling seamless integration with other cloud-native tools and services.
Teams adopting cloud-native strategies should look for registries that offer easy integration, support for multiple schema formats, and automated scaling. These features help maintain reliable data pipelines in dynamic cloud environments.
Hybrid Environments
Hybrid environments combine on-premises and cloud data streaming systems. Many organizations use this approach to balance control, security, and scalability. Selecting the right schema registry for hybrid setups ensures smooth data flow and consistent governance across both environments.
Confluent offers a strong solution for hybrid environments. Teams can use the fully-managed Schema Registry in Confluent Cloud together with the self-managed Schema Registry in Confluent Platform. This dual setup allows organizations to manage schemas consistently, whether data streams run on-premises or in the cloud.
Key features that support hybrid deployments include:
Private Networking: Schema Registry PrivateLink enables secure connections between on-premises systems and Confluent Cloud. This feature protects sensitive data and reduces exposure to the public internet.
API Key Management: Each environment can use separate API keys. This approach improves access control and helps teams track schema changes by environment.
Compatibility Modes: Teams can set compatibility rules globally or for specific subjects. This flexibility ensures that schema evolution remains safe and predictable, even when data moves between cloud and on-premises systems.
Multi-Format Support: Both environments support Avro, Protobuf, and JSON Schema. This compatibility allows teams to use their preferred serialization format without extra configuration.
Unified Management Tools: REST APIs and command-line tools work in both cloud and on-premises setups. Developers can automate schema registration, updates, and validation across the entire hybrid architecture.
The table below summarizes important features for hybrid schema registry deployments:
| Feature | Benefit for Hybrid Environments |
| Private Networking | Secure, direct connections between cloud and on-premises |
| API Key Management | Fine-grained access control per environment |
| Compatibility Modes | Safe schema evolution across both setups |
| Multi-Format Support | Flexibility for different data serialization needs |
| Unified Management | Consistent tools for automation and governance |
Tip: Teams should plan for consistent compatibility settings and governance policies across all environments. This practice helps prevent schema conflicts and ensures reliable data streaming.
Hybrid environments benefit from a schema registry that bridges cloud and on-premises systems. By using solutions like Confluent’s, organizations gain secure, unified schema management and maintain data quality as they scale.
Implementation Tips
Deployment
Teams should plan schema registry deployment with reliability and scalability in mind. They often choose between standalone, clustered, or cloud-native setups. Standalone deployments suit small teams or development environments. Clustered deployments provide high availability for production workloads. Cloud-native registries integrate with managed streaming services and object storage, supporting elastic scaling.
Deployment best practices include:
Place the registry close to Kafka brokers or streaming platforms to reduce network latency.
Use stateless agents or containers for easier scaling and maintenance.
Configure TLS encryption and authentication to protect schema data.
Monitor resource usage, such as CPU and memory, to avoid bottlenecks.
Automate deployment with CI/CD pipelines for consistent updates.
Tip: Teams should test registry failover and recovery procedures before moving to production. This step ensures real-time data pipelines remain reliable during outages.
Schema Evolution
Managing schema evolution is essential for maintaining compatibility in real-time applications. Teams must support both backward and forward compatibility to avoid breaking data contracts. They follow several strategies to achieve safe schema changes:
Adopt schema versioning to support legacy schemas and smooth transitions.
Maintain non-breaking changes for critical business attributes to ensure data consistency.
Use extensible schema designs, such as flexible fields or JSON columns, to accommodate future attributes.
Employ parallel schema management, allowing old and new schema versions to coexist before retiring legacy schemas.
Apply gradual additive changes, like adding new fields instead of modifying or deleting existing ones.
Communicate schema changes and maintain thorough documentation to align teams.
In-place schema evolution allows streams to contain events with multiple schema versions. Consumers ignore unknown fields, which ensures compatibility. Dual schema upgrades use separate streams for old and new versions, letting consumers read compatible data and retire old schemas after upgrades. Compatibility checks confirm that applications can process both old and new formats without failure.
The following table summarizes upgrade strategies:
| Compatibility Strategy | Description | Upgrade Order |
| BACKWARD / BACKWARD_TRANSITIVE | Consumers read new schemas with old code | Upgrade consumers |
| FORWARD / FORWARD_TRANSITIVE | Producers write old schemas with new code | Upgrade producers |
| FULL / FULL_TRANSITIVE | Both backward and forward compatible | Any order |
| ALWAYS_COMPATIBLE | Compatibility checks disabled | Any order |
| ALWAYS_INCOMPATIBLE | Schema evolution disabled | No upgrades allowed |
Note: Teams should document schema changes and communicate them across departments to minimize disruptions in real-time data pipelines.
Monitoring
Monitoring the health and performance of a schema registry helps teams maintain efficient real-time operations. They track several key metrics and use specialized tools for visibility.
Recommended metrics and tools include:
| Metric / Tool Name | Description |
| Active Connections | Number of active TCP connections, indicating current load and usage. |
| Request Latency | Time taken to respond to schema fetch or registration requests, useful for detecting bottlenecks. |
| Registered Schemas | Count of schemas registered, reflecting schema growth and complexity. |
| Schema Types | Distribution of schema formats, helping assess serialization variety. |
| JMX MBeans Metrics | Metrics such as connections-active, busy_thread_count, thread_pool_usage, and request_queue_size. |
| Per-Endpoint Metrics | API endpoint request metrics for detailed monitoring. |
| Monitoring Tools | JConsole or other JMX-compatible tools for browsing and monitoring exposed metrics. |
Teams also monitor:
Active connections to understand traffic and scaling needs.
Request latency to identify performance bottlenecks.
Registered schemas to manage growth and complexity.
Schema types to assess serialization usage and potential issues.
Teams should set up alerts for high latency or resource usage. Regular monitoring ensures the registry remains responsive and supports real-time data pipelines without interruption.
Selecting the right schema registry depends on several factors, including compatibility with multiple schema formats, scalability, and governance features. Startups may benefit from lightweight registries that support agile version control, while enterprises should prioritize robust schema management and integration. Cloud-native teams often require automated lifecycle management and strong compatibility checks. Teams should evaluate their streaming architecture and centralize schema management to ensure data consistency. For deeper insights, comprehensive guides and best practices on schema evolution and registry integration are available from leading platforms.
FAQ
What is a schema registry used for?
A schema registry stores and manages data schemas. Teams use it to enforce data contracts, validate messages, and track schema versions in real-time data streaming environments.
Which schema formats do most registries support?
Most schema registries support Avro, Protobuf, and JSON Schema formats. Some registries also handle API specifications or custom artifact types.
How does schema evolution work in a registry?
Schema evolution allows teams to update schemas without breaking existing data pipelines. The registry checks compatibility and supports multiple schema versions for safe upgrades.
Can small teams deploy a schema registry easily?
Small teams can deploy lightweight registries like Karapace or Apicurio quickly. These solutions require minimal resources and offer simple setup steps.
Is a schema registry necessary for Kafka?
A schema registry is not required for Kafka, but it helps maintain data quality and compatibility. Most teams use a registry to avoid data corruption and simplify schema management.
How do registries handle security?
Registries use authentication, encryption, and access controls. They protect schema data with TLS, role-based permissions, and audit logging.
What happens if a schema change breaks compatibility?
The registry blocks incompatible schema changes. Teams must fix the schema or update consumers and producers to match the new format.
Can a schema registry run in the cloud?
Many schema registries support cloud deployment. Solutions like AWS Glue Schema Registry and WarpStream BYOC allow teams to manage schemas in cloud-native environments.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Community Contribution directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
