Using Terraform, and GitHub Actions to integrate Datadog with an AWS EC2 instance
 Mary
MaryMy next task in my SheCodeAfrica Devops mentorship journey was to integrate my application with Datadog to visualize logs and traces.
Since my previous task involved using Terraform to setup an EC2 instance, I was thinking how I can add Terraform in the mix.
After various tests and checks below is what currently worked for me THIS MORNING.
Create a Datadog account and copy your default API key from Organization Settings Page.
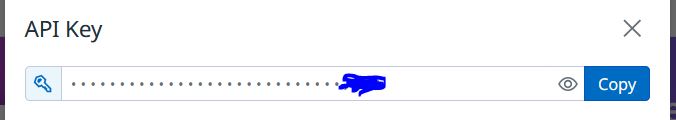
In your AWS account, generate an Access Key and Secret Access Key
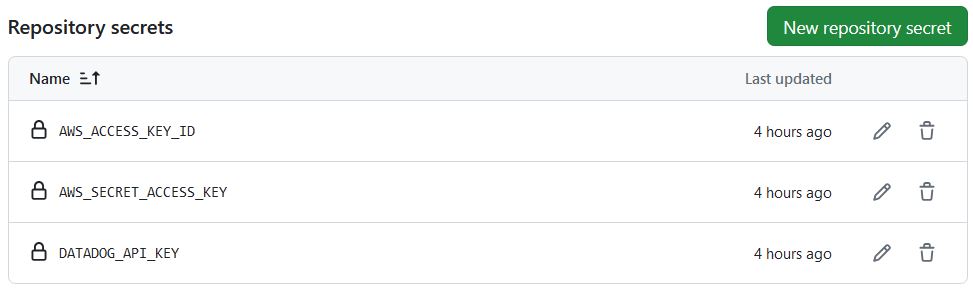
In your GitHub repo, store these 3 details as a Repository Secret.
Under Settings \> Secrets and Variables > Actions
Now create your terraform script, my example below creates an ec2 and security group, and defines a variable data_dog_api_key (more on this in the next step)
terraform { required_version = ">= 0.13" required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" } } } provider "aws" { region = "us-east-2" } variable "flask_port" { type = number default = 5000 } variable "http_port" { type = number default = 80 } variable "ssh_port" { type = number default = 22 } variable "outbound_anywhere" { type = number default = 0 } # Security Group resource "aws_security_group" "flask-terraform-sg" { name = "terraform-example-instance-3" ingress { description = "Flask" from_port = var.flask_port to_port = var.flask_port protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } ingress { description = "Webserver" from_port = var.http_port to_port = var.http_port protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } ingress { description = "SSH" from_port = var.ssh_port to_port = var.ssh_port protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } egress { description = "Outbound" from_port = var.outbound_anywhere to_port = var.outbound_anywhere protocol = "-1" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } } output "public_ip" { value = aws_instance.flask.public_ip description = "Public IP of EC2 instance" } resource "aws_instance" "flask" { ami = "ami-0862be96e41dcbf74" instance_type = "t2.micro" vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.flask-terraform-sg.id] user_data = <<-EOF #!/bin/bash DD_API_KEY=${var.datadog_api_key} DD_SITE="datadoghq.eu" bash -c "$(curl -L https://install.datadoghq.com/scripts/install_script_agent7.sh)" EOF user_data_replace_on_change = true tags = { Name = "Example" } } variable "datadog_api_key" { description = "Datadog API Key" type = string }Note that the defined ami is associated with Ubuntu operating system
You can access the datadog integration script (inside the user_data) section in the Integrations > Agent section of Datadog. Remember to choose the appropriate instruction for your ami type.
Finally define your GitHub Action Workflow file
name: 'Terraform'
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
env:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
DATADOG_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.DATADOG_API_KEY }}
jobs:
terraform:
name: 'Terraform'
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Setup Terraform
uses: hashicorp/setup-terraform@v2
- name: Terraform Init
run: terraform init
- name: Terraform Plan
run: terraform plan -var="datadog_api_key=${{ secrets.DATADOG_API_KEY }}"
- name: Terraform Apply
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main' && github.event_name == 'push'
run: terraform apply -auto-approve -var="datadog_api_key=${{ secrets.DATADOG_API_KEY }}"
The important parts are env block which define the environment variables and match them to the secrets stored in Point 3.
Notice how when we run terraform plan and apply commands we are able to refer to our Datadog API Key without making it public for others to see.
Commit and push your changes.
Post Github Action workflow, wait for sometime and your host will be visible in the Datadog Host List
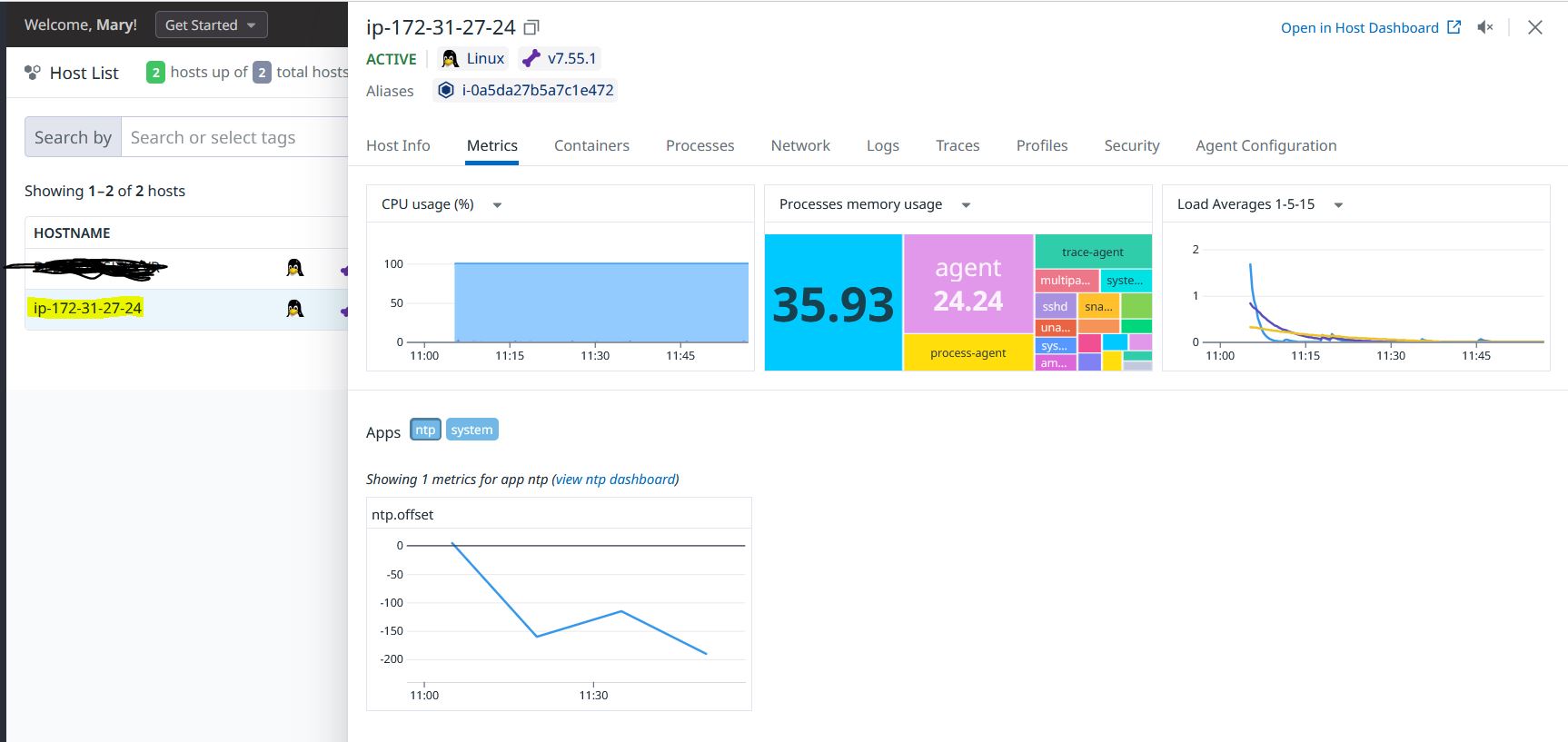
Thank you and I hope you hear how the process went through for you.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mary directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mary
Mary
Mary is a Software Engineer from Ghana. Been writing about Data Science on her blog for years. In her free time, she likes to read books and have a good rest.